The United Nations General Assembly has declared October 13th to be “International Day for Disaster Reduction”, as an effort to encourage governments in building disaster-ready infrastructure, while also raising awareness for the general public in handling disasters. As Partners might know, many patents or inventions have been created as a result of, or to deal with, urgent situations, including natural disasters.
In honor of Day of Disaster Reduction, here are five noteworthy disaster related inventions:
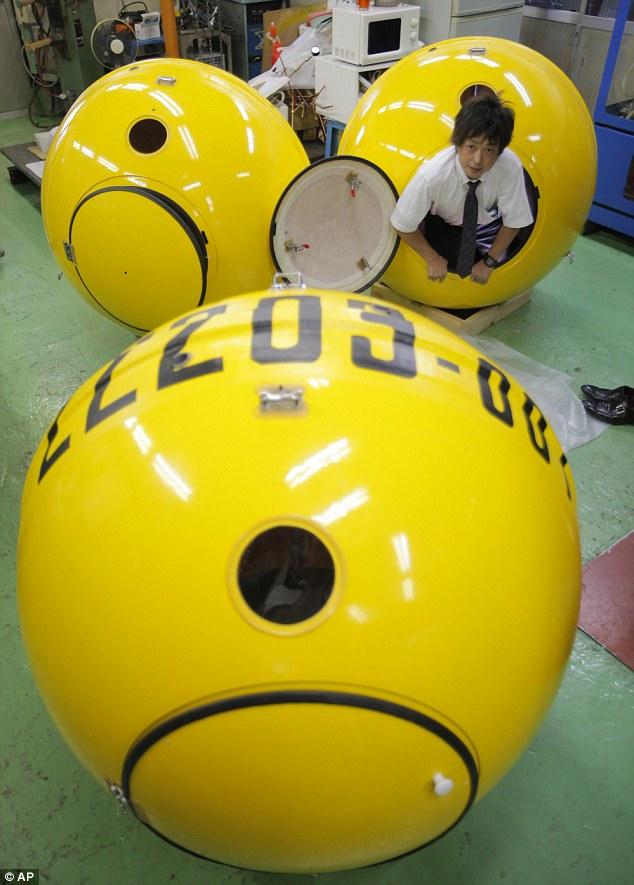
1. Noah
At first glance, this round yellow submarine may seem like it was based on the Beatles song of the name, but the name reveals that it took inspirations from religious tales, namely Noah’s Ark.
Shoji Tanaka is a Japanese businessman who was greatly affected by the Tsunami that hit his country in 2011. The phenomena drove him to create a vehicle that would help the community deal with potential future Tsunamis.
Noah consists of one hatch, one glass window and two holes for drainage and ventilation. It is made of fiber-reinforced plastic material, making it strong yet light. In addition, Noah is deliberately designed for simple use. Its spherical shape not only allows it to float in a Tsunami, but also keeps it from tipping over in case of an earthquake. In terms of size and weight, Noah is quite practical. With a diameter of about 1.2 meters, Noah can be stored at the average home while also light enough to be moved around. Lastly, the yellow color was also chosen for it to be easily detected by rescuers..
2. The All-Terrain Solar Trailer (ATST)
Natural disasters can devastate an area’s infrastructure so severely that many sources of basic needs are cut. Buildings collapsed, drains destroyed, and of course, electricity cut. Often disaster victims’ situations are made even more difficult by the lack of electricity to communicate. To tackle this, Michael and Kenny Ham designed the All Terrain Solar Trailer (ATST), a tool to maintain communication lines in disaster zones with power outages.
ATST is a portable generator station that can charge up to 100 cell phones at once, using batteries and solar power. Each unit is equipped with four or eight batteries providing 1200 to 2400 watts of solar charge, complete with 100 outlets– 50 of which are regular 110 volt outlets, while the other outlets are for various other forms of device plugs. Furthermore, as the name suggests, mobility is very important for the ATST, and it is designed to reach places where road infrastructure has been destroyed.
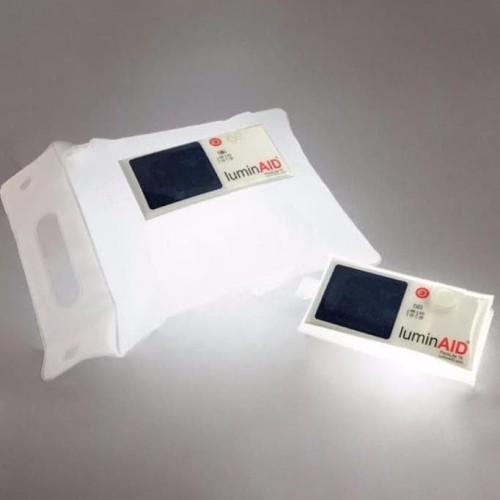
3. LuminAID
Power outages certainly not only hinder disaster victims’ ability to use phones, but also sentence them into darkness. Thus, LuminAid was created to give emergency lighting in disaster zones.
This device was created by two Columbia University architecture students, Anna Stork and Andrea Sreshta. They crafted a solar-powered and inflatable LED that is easy to carry, adaptable to various terrains, waterproof and floatable, while also offering high energy. One unit of LuminAID is capable of lighting up for upto three years.
the LuminAID company has been actively distributing their products to disaster areas as well as to other communities in need. Through their “Give Light” project, LuminAID has helped luminate various disaster zones around the world, such as the forest fire in California, floods in Malawi, earthquakes in Nepal, and so on.
4. Network based system for predicting landslides and providing early warnings
This invention by Maneesha V. Ramesh is designed to detect landslides. As explained in the patent description, this system consists of wireless node for monitoring landslide conditions with at least one tubular probe body deployed in a borehole in a landslide prone area and anchored to rock below soil, multiple sensors carried by and deployed within and or outside of the tubular probe body for measuring geologic motion and hydrologic saturation and pressure at three or more distinct levels of soil above the rock, a power source, a data acquisition board in communication with the sensors carried by and or deployed within or outside of the probe body, and a wireless transceiver in communication with the data acquisition board and accessible to a local area wireless network (LAWN), which is in turn accessible to a wide area wireless network (WAWN).
Geologic and hydrologic data of at least three separate layers of soil above the anchor rock is collected in real time from the sensors deployed on or near the probe body, the data qualified against threshold readings in three or more stages to provide graduating levels of alerts culminating in a warning of an impending landslide.
5. Public Lab (PLOTS) DIY Spectrometry Kit
Spectrometers can measure the properties of light by breaking it down into different colors to be deducted separately, so that the chemical composition of a material can be analyzed. The spectrometer is not a new invention, what makes the version by Public Lab unique is that it is designed to be usable by the general public, so that anyone can identify and analyze potential contamination of drinking water in disaster zones.
This kit is made up of a VHS box, black card paper, a DVD-R piece, and a USB webcam. As light enters the device, the grooves on the DVD create prisms that bend light waves to different degrees, resulting in a spectrum that can be analyzed. Furthermore, the kit also provides open source software that allows users to share and compare their findings.
If Partners have any questions or require any services related to Intellectual Property, please contact us via marketing@ambadar.co.id. We will ensure the best services according to your needs.
Sources: